Cloud Computing Fundamentals
In This Article, we'll discuss the Cloud Computing Fundamentals
Computing Paradigms
Basic Computing paradigms that derive the cloud are:
- Distributed Computing
- Pervasive Computing
- Utility Computing
Distributed Computing
- Method of computer handling in which various pieces of a program run all the while on at least two PCs that are speaking with one another over a system.
- It is a sort of sectioned or parallel computing in which various pieces of a program run at the same time on at least two processors that are a piece of a similar PC.
- Two computers are probably going to have distinctive record frameworks and diverse equipment parts.
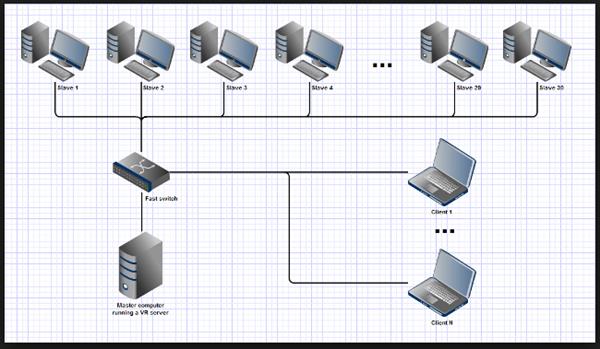
Features of Distributed Computing:
- Heterogeneity
- Openness
- Scalability
- Security
- Fault tolerance
- Concurrency
- Transparency
Distributed computing: Types
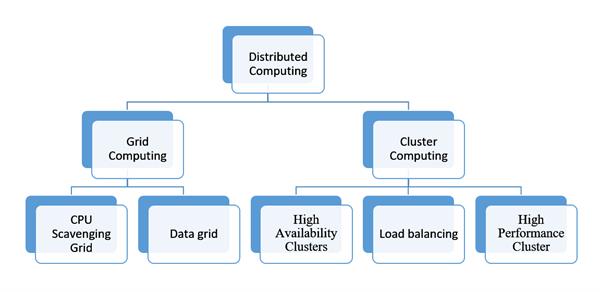
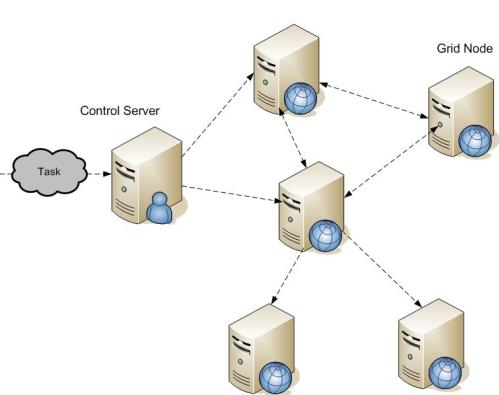
Grid Computing
- Grid computing is a processor engineering that joins computer assets from different areas to arrive at a primary target.
- In lattice registering, the computers on the system can take a shot at an errand together, hence working as a supercomputer
- Two types: Data grid and CPU searching lattice
Data grid
- A framework that handles huge informational indexes utilized for information the board and controlled client sharing.
- The Southern California Earthquake Center is a case of an information matrix; it utilizes a center programming framework that makes a computerized library, a scattered record framework and proceeding with chronicle.
CPU scavenging grid
- A cycle-rummaging framework that moves ventures starting with one PC then onto the next as required.
- A well-known CPU rummaging network is the quest for extraterrestrial insight calculation, which incorporates in excess of 3,000,000 PCs.
Cluster Computing
- A Computer bunch is a gathering of connected PCs, cooperating intently so that in numerous regards they structure a solitary Computer.
- The components of a cluster are commonly, however not constantly, associated with one another through quick neighborhood
- High Availability Clusters: High accessibility bunches (otherwise called HA bunches or failover bunches) are gatherings of PCs that help server applications that can be dependably used with at least down-time.
- Load Balancing Clusters: Load adjusting is isolating the measure of work that a PC needs to do between at least two PCs so more work completes in a similar measure of time and, when all is said in done, all clients get served quicker.
- High Performance Cluster Computing: High Performance Cluster Computing (HPCC) stores and procedures huge amounts of information, handling billions of records for every second utilizing huge parallel preparing innovation.
Utility computing
- Conventional Internet facilitating administrations have the ability to rapidly mastermind the rental of individual servers, for instance to arrangement a bank of web servers to suit an unexpected flood in rush hour gridlock to a site.
- Multiple servers are utilized on the ―back end
- ay per use services
Pervasive computing
- Pervasive registering (likewise called omnipresent processing) is the developing pattern towards inserting chip in ordinary protests so they can convey data.
- The words inescapable and omnipresent signify "existing all over the place." Pervasive figuring gadgets are totally associated and always accessible.





